Main Idea
The rapid growth of social media platforms has brought about various changes in the way we interact with the world. While social media allows for connection and entertainment, it has also raised concerns regarding its impact on mental health. This study focuses on examining the relationship between social media usage and mental health indicators, particularly in the context of young adults. The hypothesis is simple: social media usage—especially among young adults—correlates with negative mental health outcomes such as restlessness, depression, and difficulty concentrating. By analyzing data on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube, we aim to understand whether this hypothesis holds true.
Understanding the Requirements
Let’s inspect the dataset to understand its structure and characteristics.
After loading the data, we noticed that some columns contained missing values and others had categorical variables that needed conversion into numerical formats. We also identified and prepared columns that represented social media platform usage and mental health indicators.
Load & Inspect the Data
This step involved loading the dataset and inspecting its structure. We performed several important tasks:
– Identifying missing values and checking data types.
– Handling missing values by removing rows with missing data.
– Converting categorical variables (such as Yes/No responses) into numerical values (0 or 1).
Data Preparation
We focused on cleaning the data and transforming it into a usable format for analysis:
– Handling missing data and transforming categorical variables.
– Addressing outliers, especially in the Age column, and segmenting age into three groups (18-34, 35-54, 55+).
– Converting platform usage (Facebook, Instagram, YouTube) into numeric data for easier analysis.
Data Analysis & Exploration (EDA)
we performed exploratory data analysis (EDA) to uncover key insights about the relationships between social media usage and mental health indicators:
– Group Analysis: We conducted t-tests to assess the differences in mental health indicators between users and non-users of each platform (Facebook, Instagram, YouTube).
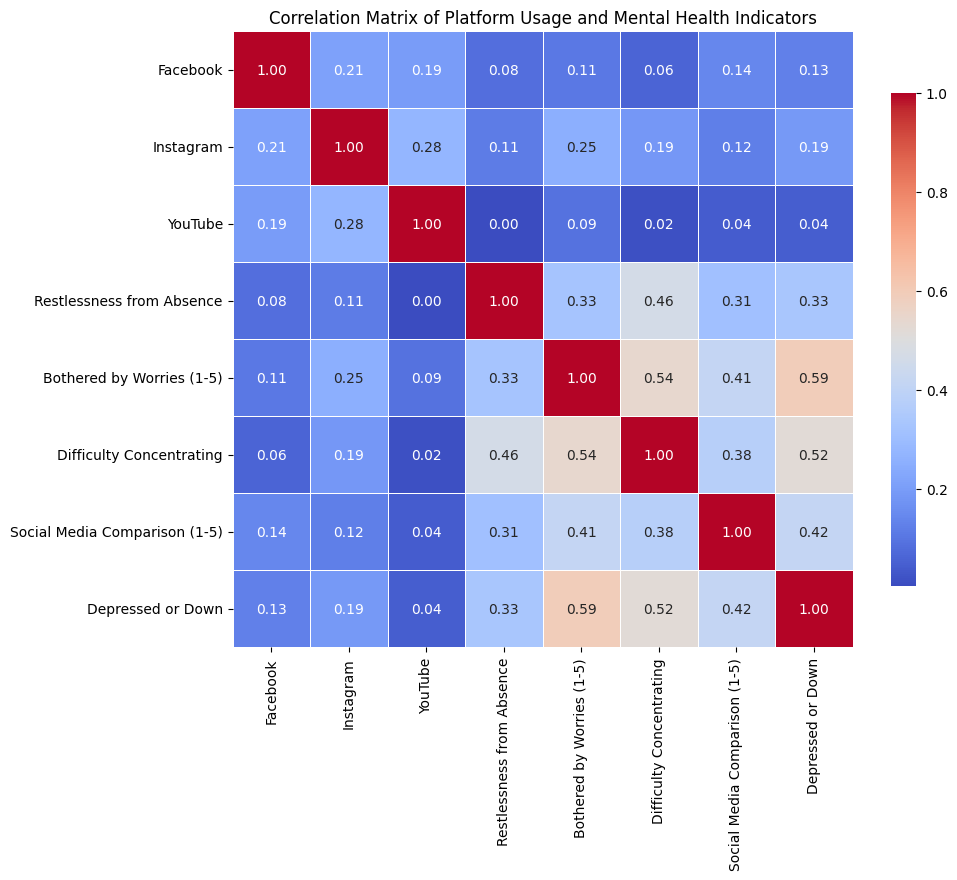
– Correlation Analysis: We calculated the correlation matrix to examine relationships between platform usage and mental health.
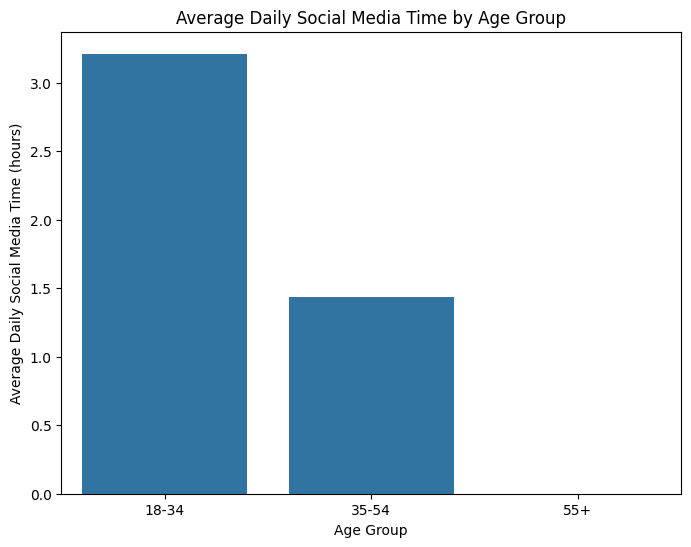
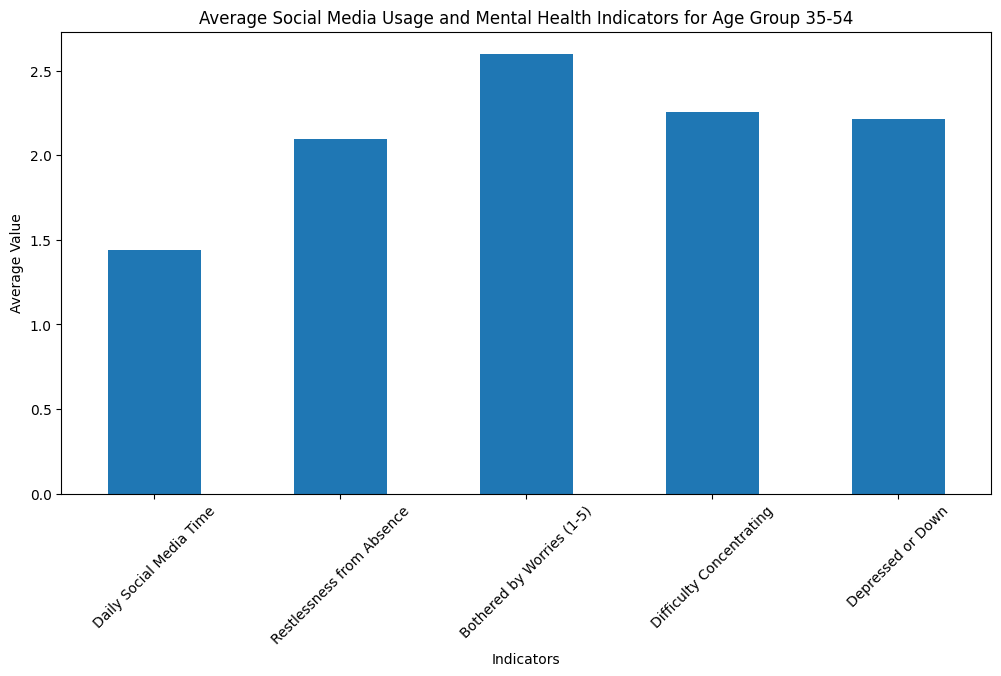
– Grouped Analysis by Age: We segmented the data by age groups (18-34, 35-54, 55+) to analyze social media usage and mental health patterns.
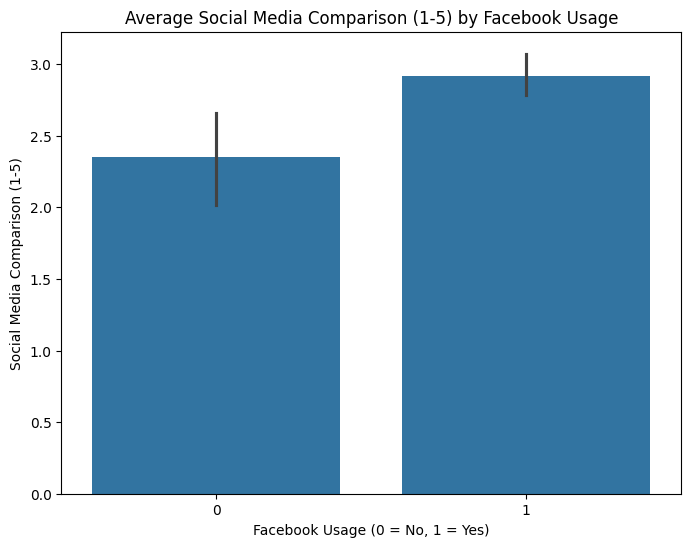
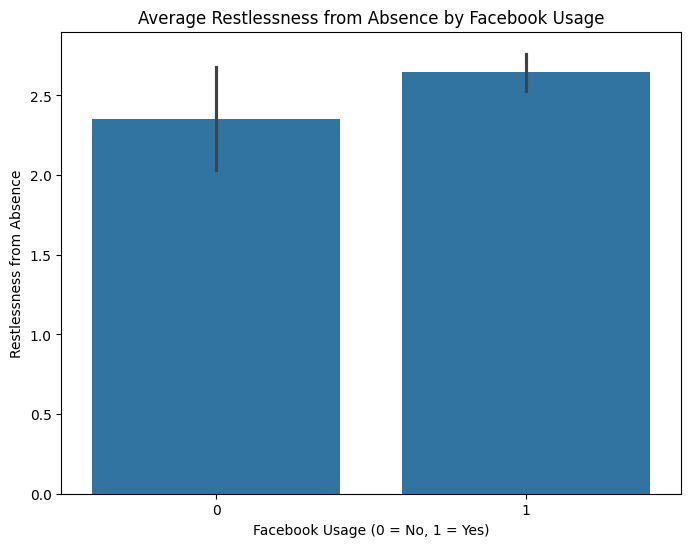
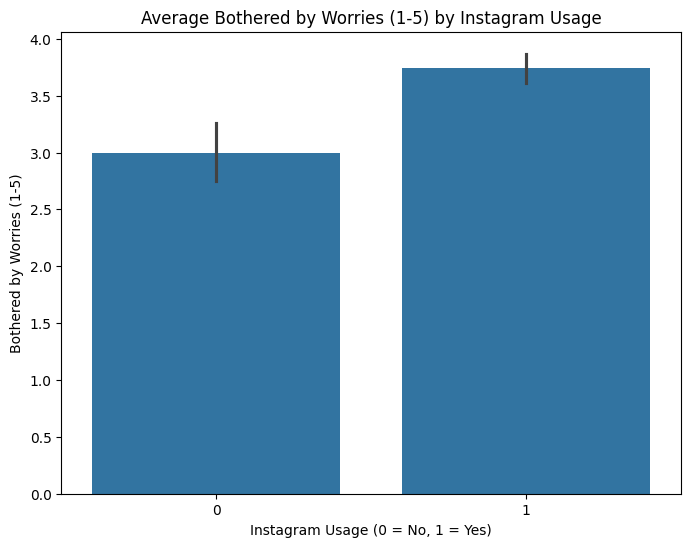
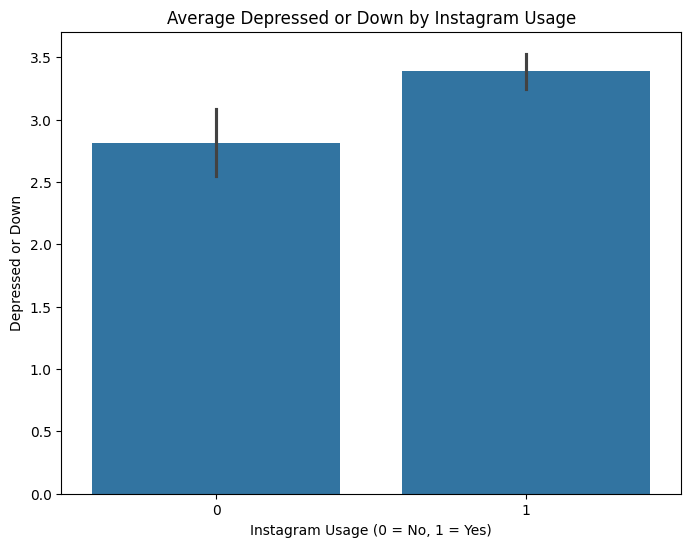
Group Analysis Visualization
Bar plots were created to visualize the average mental health indicators across users and non-users of each platform. This allows us to see the comparative differences in indicators like restlessness, depression, and concentration.
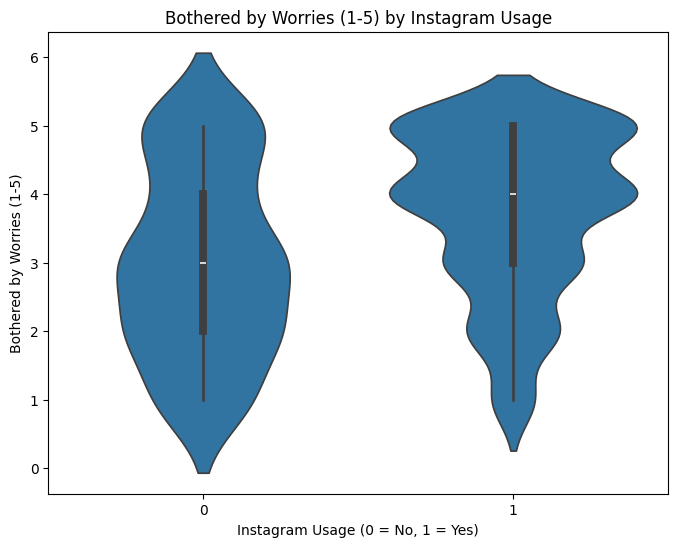
Violin Plots for Social Media Usage vs Mental Health
Violin plots were used to show the distribution of mental health indicators for platform users and non-users. These plots provide insights into the spread of data and highlight any outliers or trends in the dataset.
Summary
Based on the analysis, it is evident that social media usage, particularly among young adults (18-34), is correlated with higher levels of mental health issues. Our findings indicate that Instagram users, in particular, show a significant correlation with increased social media comparison, leading to higher depression levels. This supports the hypothesis that higher social media usage, especially among young adults, leads to negative mental health outcomes.
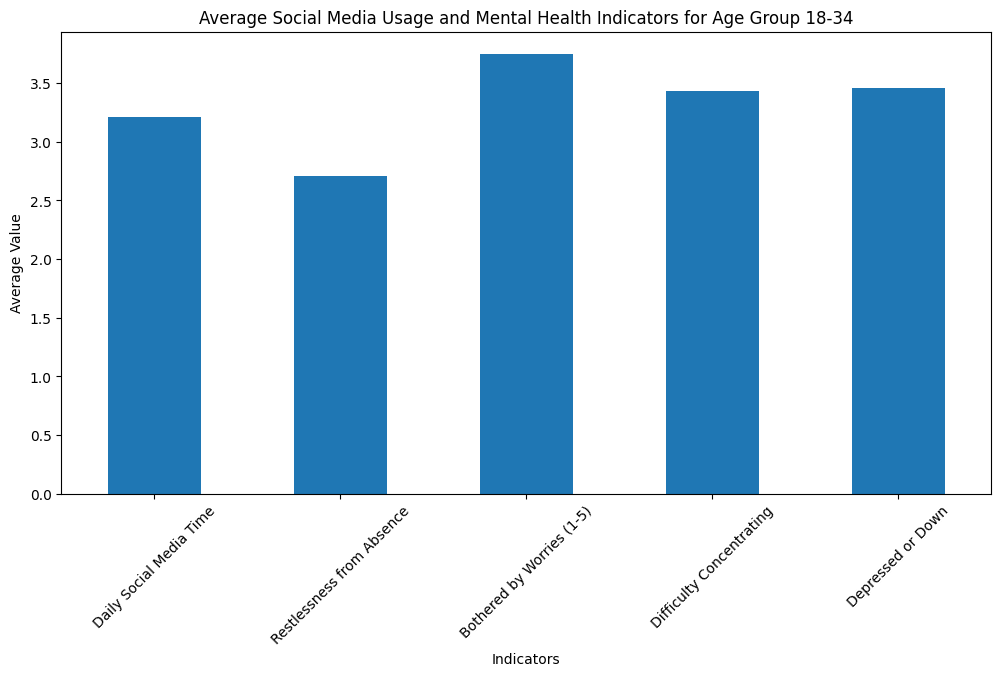
Advice for Young Adults
To help manage the negative psychological effects of social media, here are a few practical tips for young adults:
- Limit Screen Time: Be mindful of your social media usage. Try to set limits on your daily screen time.
- Be Aware of Social Media Comparison: Recognize that the content you see on social media is often curated and does not reflect reality.
- Take Breaks: Engage in offline activities—whether it’s reading, exercising, or spending time with family and friends.
- Follow Positive Influences: Make an effort to follow accounts that promote mental health awareness, self-care, and positive lifestyles.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you feel overwhelmed or notice a decline in your mental health, it’s important to reach out to a professional.
